Definition
What It Does
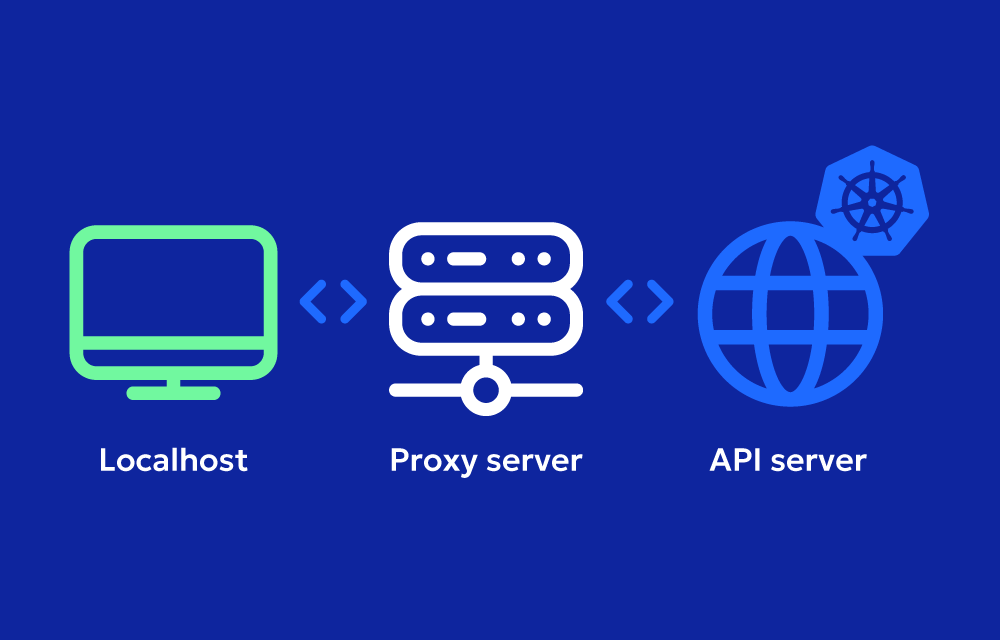
When you run kubectl proxy, it starts a local HTTP server that handles authentication and communicates with the Kubernetes API server on your behalf. This allows you to access cluster resources via REST API endpoints without needing to handle tokens or certificates manually.
How to Use kubectl proxy
Basic Command
kubectl proxy
This starts a proxy server at http://localhost:8001/ by default.
Accessing the Kubernetes API Through the Proxy
Once the proxy is running, you can use a web browser or a tool like curl to access cluster information. For example:
curl http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods
This returns a list of pods in the default namespace.
Use Cases
- Browsing the Kubernetes Dashboard (if deployed):
Access it at:http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kubernetes-dashboard/services/https:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/ - Testing custom API clients or integrations:
You can test calls to the Kubernetes API locally without managing tokens or certificates. - Inspecting live API data for learning or debugging:
Easily fetch raw JSON data from various Kubernetes API endpoints.
Advanced Options
kubectl proxy --port=8888 --address=0.0.0.0 --accept-hosts='^.*$'
--port=8888: Changes the port from the default 8001 to 8888.--address=0.0.0.0: Allows access from external hosts (not just localhost).--accept-hosts='^.*$': Accepts all hostnames. Use with caution for security reasons.
Security Consideration
By default, kubectl proxy only accepts connections from localhost and does not require additional authentication, relying on your local kubeconfig for access. Do not expose this proxy to the internet, especially with the --address=0.0.0.0 flag, unless you fully understand the security implications.
See Also
kubectl get– for querying resources directly from the command line.- Kubernetes API Reference – for available API paths.