Node Hibernation is similar in concept to the sleep mode on personal computers, where the system state is saved, and the machine is powered down. When reactivated, it picks up immediately from where it was paused. This capability is particularly useful in cloud environments where cost optimization is a priority.
How Does Node Hibernation Work?
The hibernation process involves several key steps:
- Memory State Preservation – When a node is hibernated, its RAM contents are written to persistent storage. This includes all running processes, memory caches, and system states.
- Resource Release – CPU and RAM resources are released back to the cloud provider, reducing costs. Persistent storage, however, remains allocated to preserve the state.
- Persistent Storage Handling – Attached volumes (EBS in AWS, Persistent Disks in GCP, Managed Disks in Azure) continue to hold data during hibernation.
- Reactivation and Restoration – When reactivated, the memory state is reloaded from storage, and the node resumes as if it had never been paused.
Example Use Cases
- Development and Testing Environments: Development servers can be paused during off-hours to save costs and resumed in seconds during work hours.
- Batch Processing: Compute nodes processing batch jobs can be paused when not in use and reactivated when jobs are queued.
- Disaster Recovery: Systems in disaster recovery configurations can be hibernated and instantly reactivated during failover events.
- Analytics Workloads: Data analysis workloads can be paused during data gathering and resumed during processing.
Key Benefits
- Cost Efficiency: Idle instances do not consume compute resources, significantly lowering cloud costs.
- Operational Continuity: Applications resume exactly where they left off, with all memory, configurations, and network states intact.
- Faster Startup Times: Hibernation is faster than booting a new instance from scratch, often reducing downtime.
- Resource Optimization: By hibernating nodes during off-hours or idle times, organizations maximize resource utilization.
Challenges of Node Hibernation
While Node Hibernation is effective, it comes with its own set of challenges:
1. Reactivation Time
- Traditional hibernation methods often take several minutes to restore memory states, which can be problematic for latency-sensitive applications. For instance, AWS EC2 Hibernate can take up to several minutes to fully restore depending on instance size and memory usage.
2. Memory State Corruption
- If the memory state is not saved correctly or becomes corrupted during storage, the instance may fail to restore properly, resulting in data loss or system crashes.
3. Compatibility Limitations
- Not all cloud providers or instance types support hibernation. Some operating systems and configurations may require additional setup to enable hibernation capabilities.
4. Cost of Persistent Storage
- While compute costs are reduced, persistent storage remains allocated, incurring costs. For example, AWS charges for the EBS volumes that store memory snapshots during hibernation.
Tools Supporting Node Hibernation
Several tools support node hibernation in cloud environments:
- AWS EC2 Hibernate: Allows AWS EC2 instances to pause and resume with their memory state intact.
- GCP Suspend/Resume: Google Cloud supports instance suspension, maintaining state for later reactivation.
- Azure Virtual Machine Hibernate (Preview): Azure currently provides this feature as a preview for certain VM types.
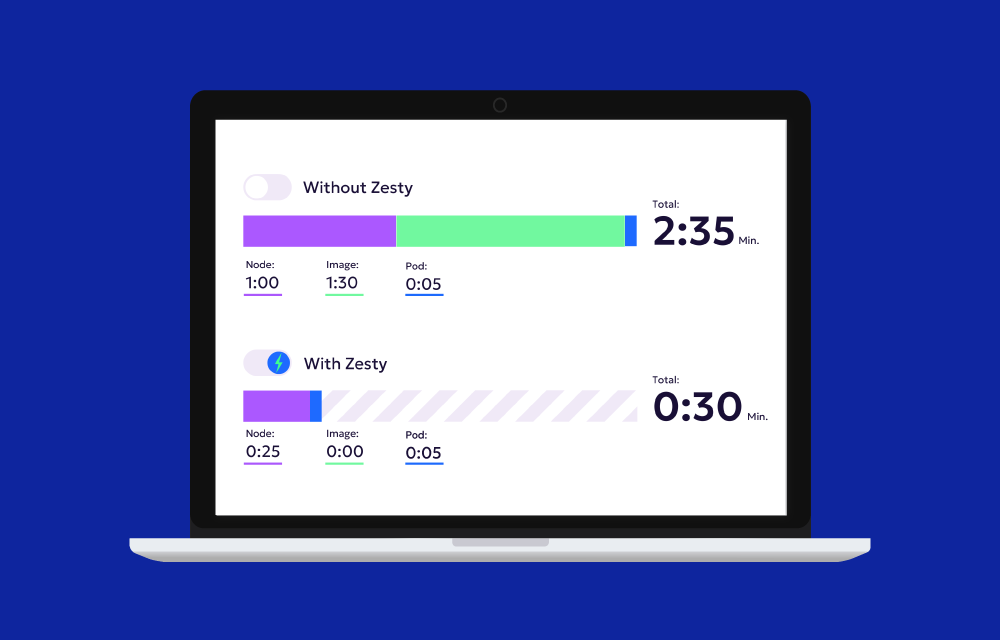
- Zesty HiberScale: Zesty’s HiberScale revolutionizes node hibernation with reactivation times of less than 30 seconds. This is a significant improvement over traditional methods, enabling high-performance applications to minimize downtime while optimizing costs.
Conclusion
Node Hibernation offers a powerful solution for optimizing cloud costs by pausing instances during idle times. Traditional solutions often face challenges like slow reactivation times and persistent storage costs. However, innovative technologies like Zesty’s HiberScale are redefining hibernation with rapid reactivation, making it a viable option for latency-sensitive and high-performance workloads.
With the right tools and configurations, Node Hibernation can be a key strategy in modern cloud optimization, reducing waste and enhancing efficiency across multiple cloud platforms.